How to Fix "DNS Server Not Responding" on Windows 10/11

If you're seeing the error message "DNS Server Not Responding," here's how to fix it quickly.
Method 1: Clear the DNS Cache
- Press Win + R on your keyboard.
- A Run dialog box will appear.
- Type cmd and click OK.
- A black Command Prompt window will open.
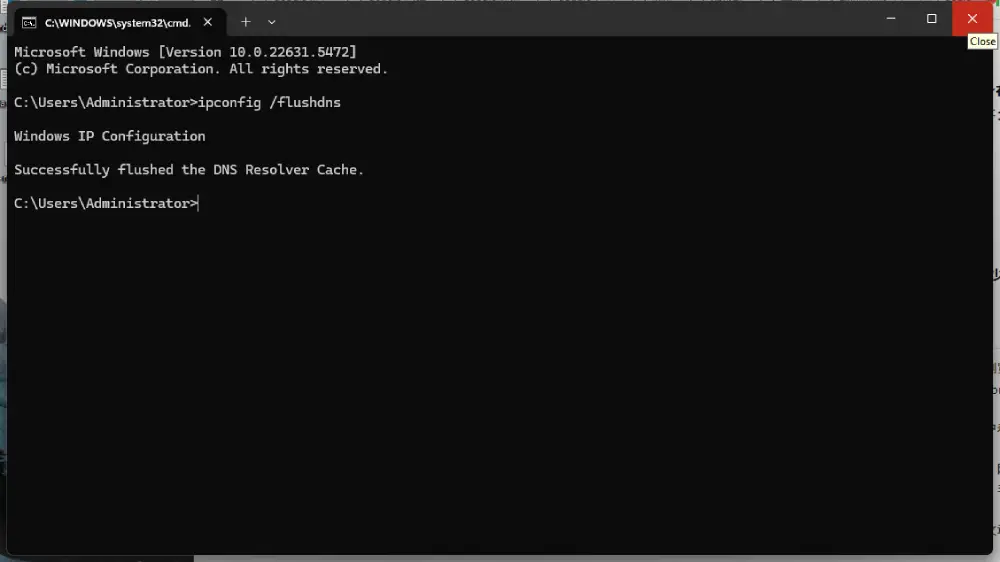
- Type the following command and press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdns- If the command runs successfully, you'll see the message:
Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache.- Close the Command Prompt window and open your browser to check if the problem is resolved.
Method 2: One-Click Quick Fix – Use Our DNS Server Fix Tool
Use our DNS Server Repair Tool to instantly flush the DNS, reset Winsock, and restore your connection.
- Click to download and save the tool.
- Double-click the downloaded DNS Server Fix Tool to open it.
- Click "Run".
- Open your browser and check if the connection has been restored.
Method 3: For Recurring "DNS Server Not Responding" Issues
Part 1: Manually Change Your DNS Server Address
- In the bottom-right corner of your screen, right-click the network icon (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and select "Network & Internet Settings."
- In the window that appears, click on "Advanced network settings" (usually at the bottom).
- You should now be in "Network & Internet > Advanced network settings".
- On the latest version of Windows 11, click "Network adapters" at the top.
- On older versions, scroll down and click "More network adapter options." - Locate the network you're currently using (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Left-click your active network connection.
- Click on "View additional properties".
- At the top of the page, find "IP assignment" — it will likely say "Automatic (DHCP)". Click the "Edit" button on the right.
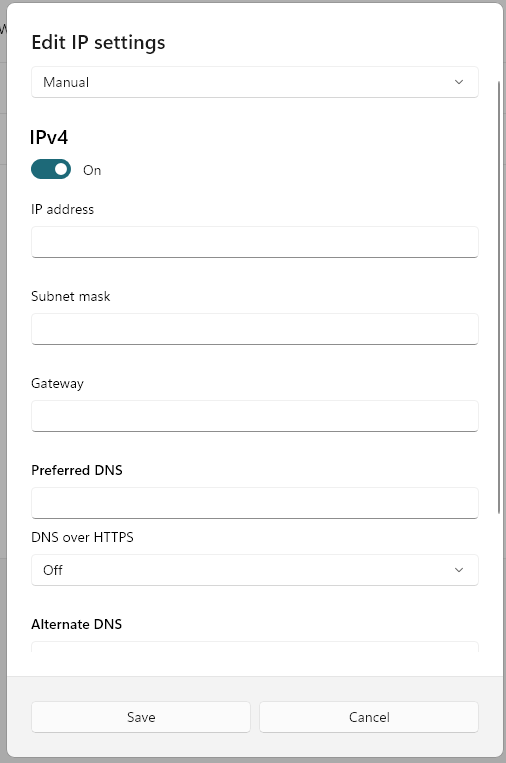
- A window titled "Edit IP settings" will appear. Change the setting from "Automatic (DHCP)" to "Manual".
- Turn on the switch for IPv4 — it should turn blue when enabled.
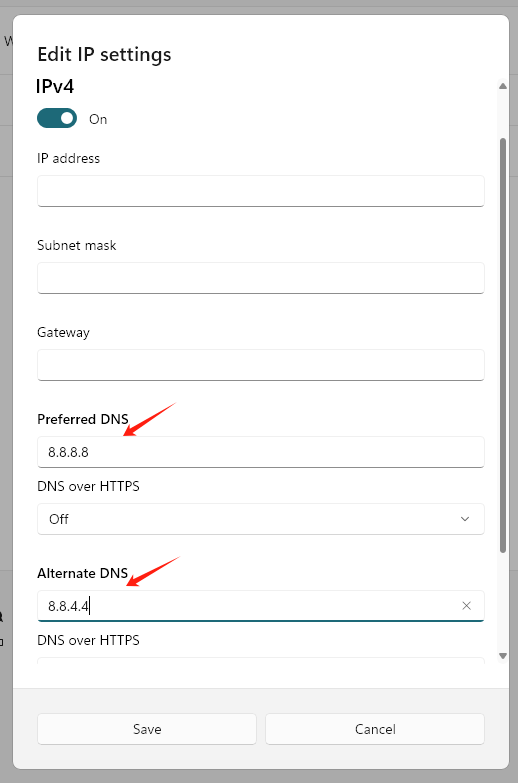
- You'll now see fields for "IP address", "Subnet prefix length", "Gateway", "Preferred DNS", "Alternate DNS", and options for DNS over HTTPS.
- Only fill in the DNS fields:
- Preferred DNS: 8.8.8.8
- Alternate DNS: 8.8.4.4
Leave all other fields as they are. - Click "Save" and close the window.
Part 2: Flush the DNS Cache
This is the same process as in Method 1:
- Press Win + R on your keyboard.
- Type cmd and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following and press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdns- You should see: "Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache."
- Close the Command Prompt and try accessing a website in your browser.
What Does "DNS Server Not Responding" Actually Mean?
First, what is DNS?
DNS stands for "Domain Name System".
The internet is essentially a network of numbers — every website has a specific "phone number" called an IP address (for example, 175.218.160.141).
These IP addresses are the unique numerical identifiers that computers use to recognize and communicate with each other.
Because numbers are hard to remember and not user-friendly, we use domain names like www.google.com, www.youtube.com, and www.facebook.com instead.
That's where DNS comes in — it acts like a phonebook or navigator of the internet, helping translate human-friendly domain names into machine-readable IP addresses.
What Does DNS Do?
- When you enter a website address, such as www.facebook.com,
- The DNS translates that domain name into its corresponding IP address — like the "phone number" we mentioned earlier.
- Your computer then uses that IP address to connect to the correct server, and the website you want to visit loads in your browser.
What Causes the "DNS Server Not Responding" Error?
- DNS Server Outage
This is one of the most common root causes.
If the DNS server you're using experiences a failure or technical issue, it won't be able to process your requests — resulting in the "DNS Server Not Responding" error.
This is usually temporary and often resolves on its own. - Network Connection Issues
Sometimes the issue lies within your own network.
A faulty router, weak signal, or a broken internet connection can prevent your device from communicating with the DNS server. - Firewall or Third-Party Software Blocking DNS
In some cases, your firewall or security software might mistakenly identify DNS requests as unsafe and block them, preventing communication with DNS servers. - DNS Cache Problems
Both your router and computer cache DNS results to improve speed.
However, if the cache becomes outdated or corrupted, it can cause DNS errors and lead to the "DNS Server Not Responding" message. - Incorrect Computer DNS Settings
If you or someone else accidentally misconfigured your DNS settings — for example, by entering an invalid DNS server address — it can prevent your computer from connecting to the internet properly. - ISP Issues
Sometimes the problem is not on your end. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) may be experiencing DNS-related issues. In such cases, it's best to contact their customer support directly.
How to Fix "DNS Server Not Responding"
Restart Your Modem, Router, and Computer
- Turn off your router and modem, wait for 3–5 minutes, then turn them back on. This clears temporary errors or cached data and often resolves DNS issues.
- Restart your computer. Though it's not always effective, it's a simple step that sometimes helps.
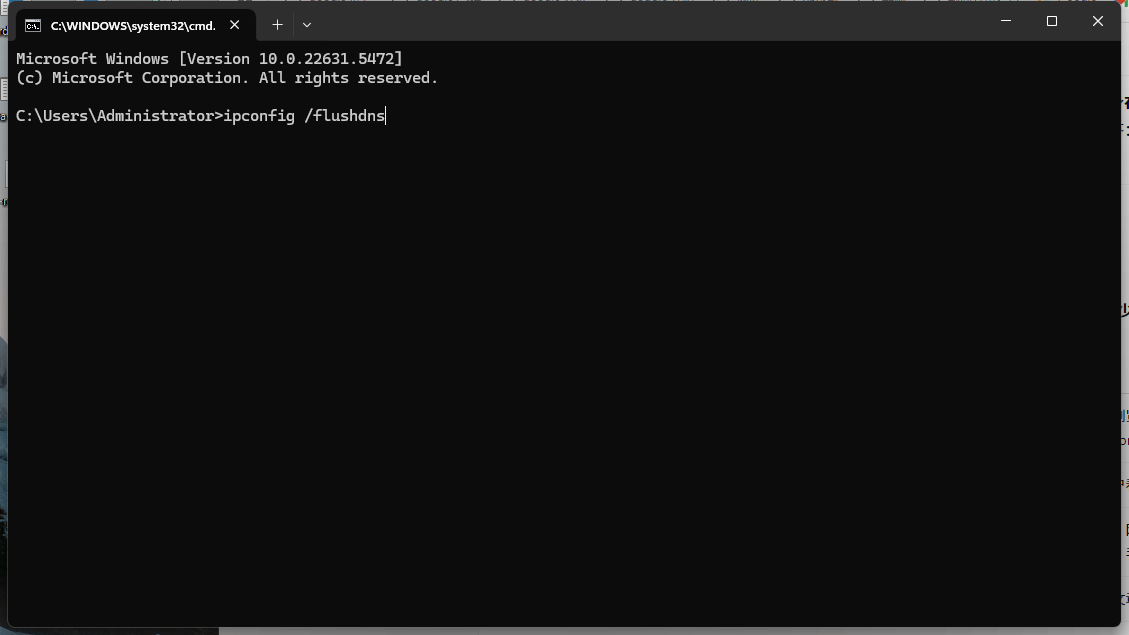
Clear DNS Cache on Your Computer
If your DNS cache is corrupted or outdated, it can cause DNS errors.
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type cmd and click OK.
- In the Command Prompt window, type:
ipconfig /flushdns- If successful, you'll see: "Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache."
- Close the window and try browsing the web again.
Update Your DNS Server Address
- Right-click the network icon and select "Network and Internet settings".
- Go to "Advanced network settings", then click "Network adapters", and select your active connection.
- Click "Edit" next to "IP assignment".
- In the popup window, select "Manual", then enable IPv4.
- Enter the following:
- Preferred DNS: 8.8.8.8
- Alternate DNS: 8.8.4.4
Leave all other fields as they are. - Save and close the window.
- After updating, you must flush your DNS cache again using:
ipconfig /flushdns- Try accessing a website in your browser.
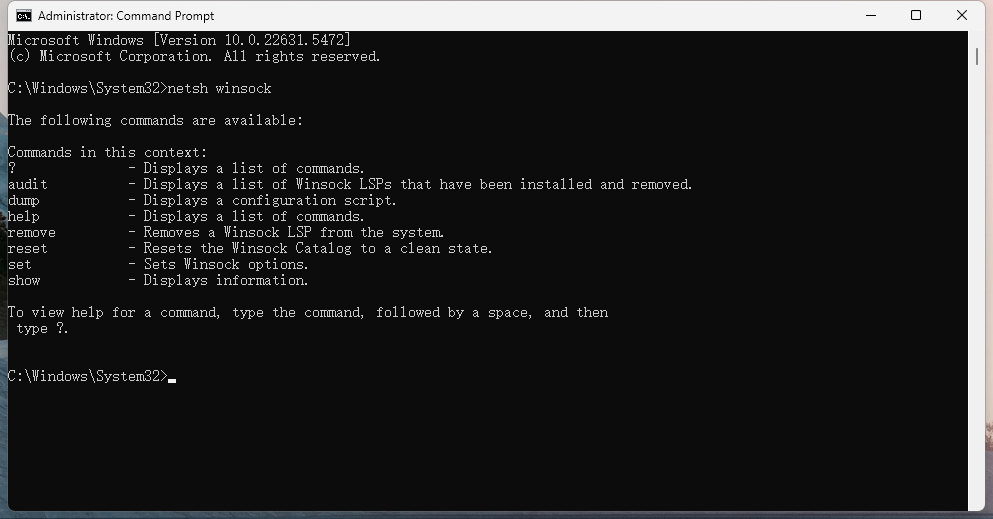
Reset TCP/IP and Winsock
- If TCP/IP or Winsock is corrupted, a reset can help.
- Open the Start menu, type "cmd", right-click Command Prompt, and select "Run as administrator".
- In the window, type the following and press Enter after each:
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Check Firewall and Third-Party Security Software
- Sometimes firewalls or third-party antivirus software block DNS requests. Try temporarily disabling them to see if they're the cause.
- To turn off Windows Firewall:
- Go to Start → search for "Windows Defender Firewall" → open it
- Click "Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off"
- Turn it off for both private and public networks
- If websites load after this, your security software was likely blocking DNS.
- Regardless of whether it fixes the issue, make sure to re-enable your firewall and antivirus afterward.
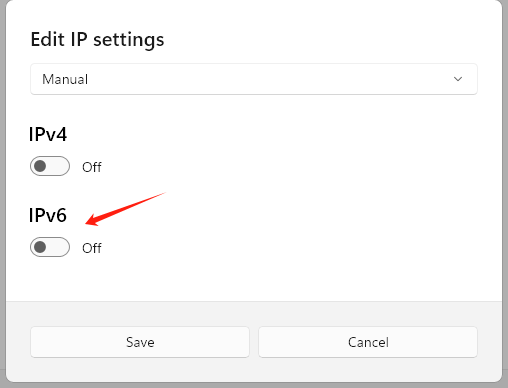
Disable IPv6
- Follow the steps: Right-click the network icon → "Network and Internet settings" → "Advanced network settings" → your active connection.
- Click "Edit" under IP settings, choose "Manual", and make sure IPv6 is switched off.
- Save and try accessing a website. This issue is rare, but it's worth checking just in case.
Update or Reinstall Network Drivers
- Open the Start menu and search for "Device Manager".
- In Device Manager, expand "Network adapters", find your active network adapter, right-click and select "Update driver".
- If that doesn't help, right-click again and select "Uninstall device", then restart your computer.
Windows will automatically reinstall a generic network driver. - Test your connection in a browser.
Contact Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- If none of the above steps resolve the issue, the problem may be with your ISP.
- Contact your ISP's customer support, provide your account details and location.
- They may send a technician to check your connection.
Why Does Clearing the DNS Cache Help?
- When you experience the "DNS Server Not Responding" error, clearing the DNS cache (via the ipconfig /flushdns command) can help.
- This command forces your system to delete all locally stored DNS records.
- The next time you visit a website, your system will have to request the latest IP address from the DNS server.
- If the problem wasn't with the DNS server itself, you should now receive the correct, up-to-date IP address.
- As a result, the website should load properly.
Summary:
Clearing your DNS cache helps bypass local DNS issues and forces your computer to fetch the latest DNS information — resolving many cases of the "DNS Server Not Responding" error.
"DNS Server Not Responding" – Frequently Asked Questions
- What does "DNS Server Not Responding" mean?
This error indicates that your device is unable to communicate with the DNS server, which is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses. As a result, websites fail to load in your browser. - How do I fix "DNS Server Not Responding" on Windows 10/11?
You can fix the issue by restarting your router, changing your DNS settings to a public server like 8.8.8.8, or running the command:For a quick and automatic solution, use the DNS Server Fix Tool to reset your network settings with one click.ipconfig /flushdns - Why is my internet not connecting to the DNS server?
This is usually caused by incorrect DNS settings, a corrupted DNS cache, a malfunctioning router, or interference from antivirus or firewall software.
In most cases, flushing the DNS or using a DNS Server Fix Tool can resolve the problem. - How do I reset DNS settings back to default?
To manually reset DNS settings, open Command Prompt and run the following commands:Alternatively, you can use the DNS Server Fix Tool to safely apply all these fixes automatically.ipconfig /flushdns netsh int ip reset netsh winsock reset - Is it safe to flush the DNS cache on Windows?
Yes. Flushing the DNS cache is a safe and commonly used troubleshooting step.
It clears outdated or corrupted DNS records and can help improve connectivity.
It does not affect your files, apps, saved passwords, or your IP address. - How can I check if my DNS is working or corrupted?
Open Command Prompt and run either of the following tests:If you receive timeouts or lookup failures, your DNS may be corrupted and should be flushed or repaired.nslookup google.com ping 8.8.8.8
Summary:
How to Fix "DNS Server Not Responding" on Windows 10/11
In this article, we've covered a wide range of methods to fix the "DNS Server Not Responding" error — from simple solutions to more advanced troubleshooting steps.
Keep in mind that not every fix works for everyone, since the cause of the issue can vary from case to case.
That's why it's important to identify your specific situation before trying different solutions.
Making random changes might make things worse rather than better.
Hopefully, this guide has helped you understand the problem and resolve it effectively.
Quick Fix (One-Click): Use our DNS Server Fix Tool to fix DNS errors in under 60 seconds — no technical skills required.